Webhooks
Receive events from all BlindPay updates.
What are Webhooks?
Webhooks are a way to receive events from all BlindPay updates. This means that for every receiver created, bank account created and every payout event, you will receive all the data in real time.
These are all the events that you can receive:
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| bankAccount.new | Triggered when a bank account is created |
| receiver.new | Triggered when a receiver is created |
| receiver.update | Triggered when a receiver is updated |
| payout.new | Triggered when a payout is started |
| payout.update | Triggered when a payout receive an update |
| payout.complete | Triggered when a payout is completed, failed or refunded |
| payout.partnerFee | Triggered when a payout is completed and a partner fee is delivered |
| payin.new | Triggered when a payin is started |
| payin.update | Triggered when a payin receive an update |
| payin.complete | Triggered when a payin is completed or failed |
| payin.partnerFee | Triggered when a payin is completed and a partner fee is delivered |
Creating a webhook
Before creating a webhook, you need to:
Now you can go to the BlindPay Dashboard, select an instance and click on the Webhooks tab.
If you just want to check if the events are being triggered, you can use Webhook Cool, a testing tool which will provide you an unique URL to receive the events.
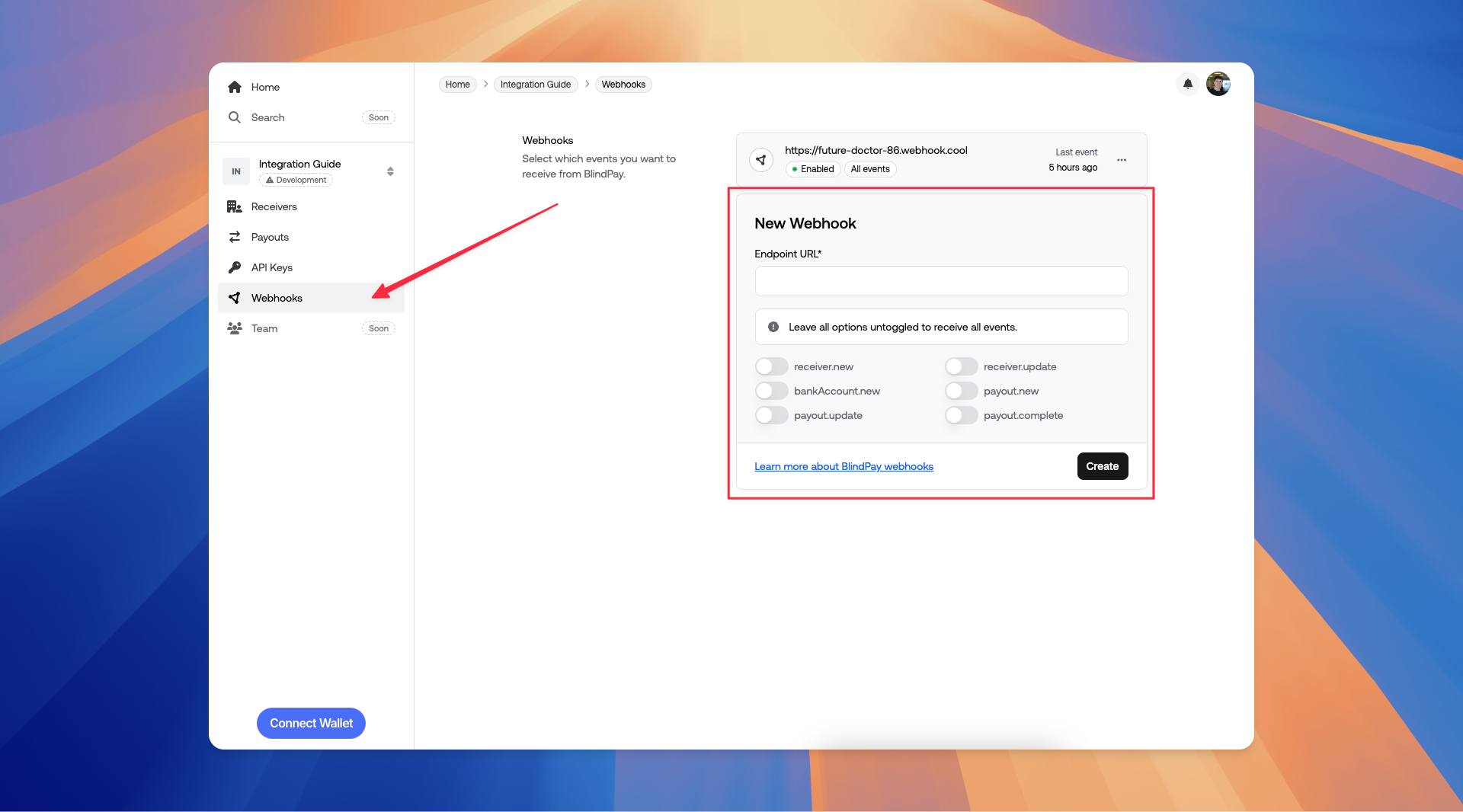
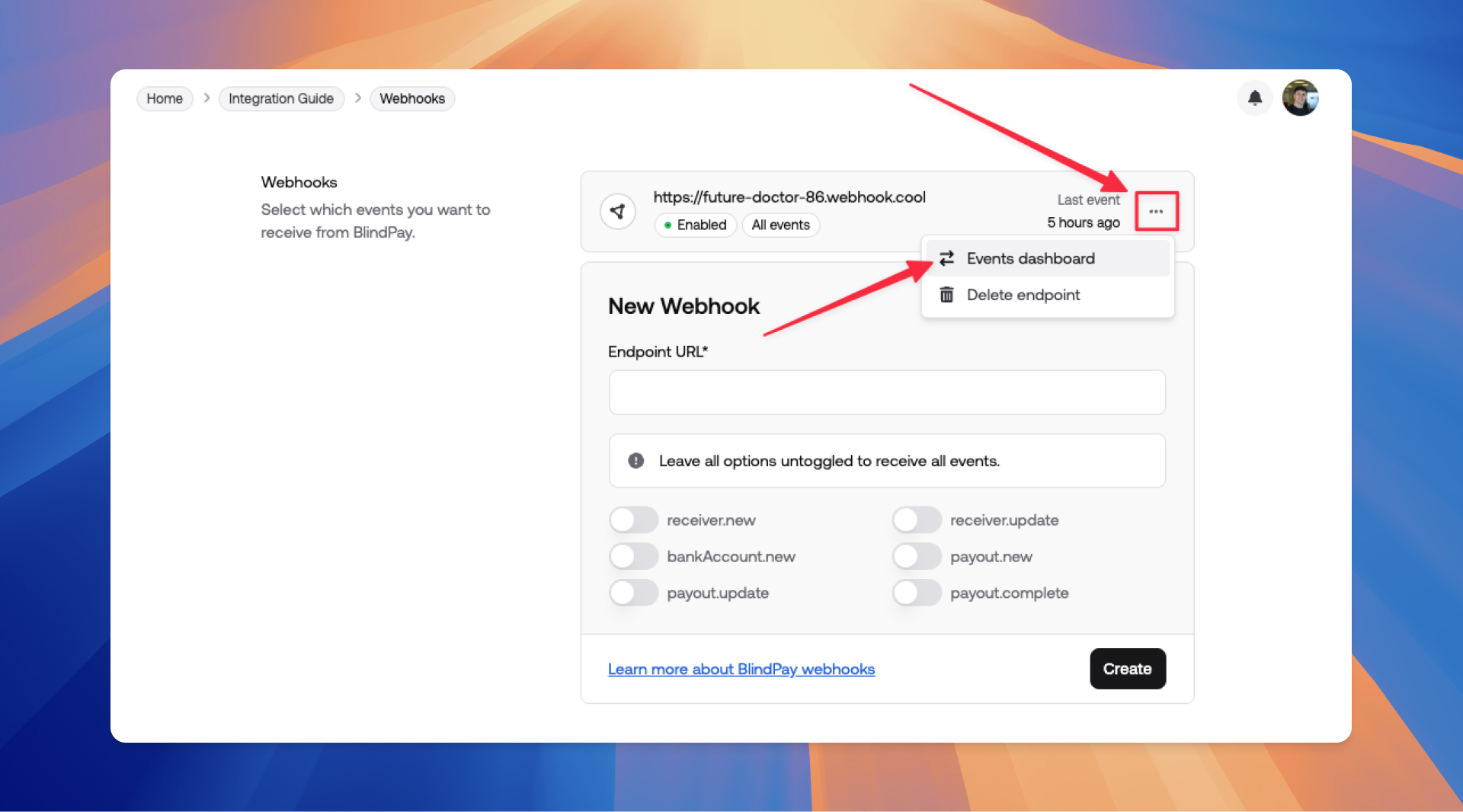
If you want to check all the events triggered by BlindPay or retry some event that you want to receive again, you can go to Events dashboard.
Verifying webhooks
Each webhook call includes verification headers to ensure the request is authentic and hasn't been tampered with.
Headers
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
svix-id | Unique message identifier (same when webhook is resent) |
svix-timestamp | Timestamp in seconds since epoch |
svix-signature | Base64 encoded list of signatures (space delimited) |
Verification Process
Construct the signed content by concatenating the id, timestamp, and payload:
Calculate the expected signature using HMAC-SHA256:
Compare signatures from the svix-signature header:
- The header contains space-delimited signatures with version prefixes
- Example:
v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE= - Remove the version prefix (e.g.,
v1,) before comparing - Use constant-time string comparison to prevent timing attacks
Verify timestamp to prevent replay attacks:
- Compare
svix-timestampagainst your system time - Ensure it's within your tolerance window
Example Verification
To get your secret you need to go to BlindPay Dashboard > Open your instance > Webhooks > Click on the ellipsis button and click on Get secret.
Never modify the request body before verification, as even small changes will invalidate the signature.